NBIP-VPNS provides secure, reliable transport of Agency applications across a contractor's multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) backbone infrastructure for geographically dispersed Agency locations. The service footprint covers CONUS, OCONUS and Non-Domestic locations. NBIP-VPNS is equivalent to FTS2001 services such as Private IP (PIP), Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), and Very high performance Backbone Network Service (VBNS).
A virtual private network (VPN) is a network that is layered on top of an underlying transport network. The private nature of a VPN derives from the implementation of the VPN in an encapsulated form that is not visible to the underlying network. Virtual paths called 'tunnels' are established within the network. The main characteristic of a Network-based VPN is that all devices involved in building the VPN are systems owned by the contractor and located at the edge of the contractor's backbone. Tunnels usually terminate at the contractor's edge router.
The following diagram illustrates a layered architecture for NBIP-VPNS with its basic building blocks. The figure shows two independent network based VPNs interconnecting Agency sites with various forms of dial, broadband, and dedicated access to the contractor's network.
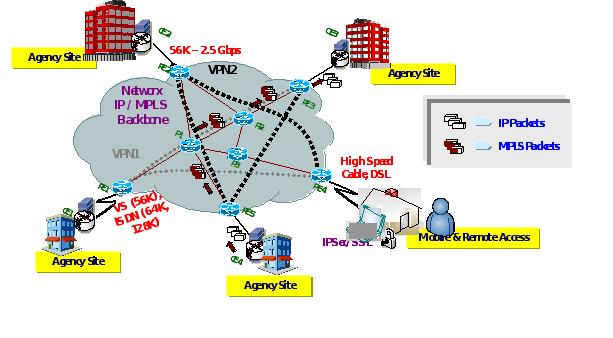
The basic building blocks are comprised of the following:
MPLS is a labeling scheme that is used by a network edge router to create paths across the network with specific constraints, such as acceptable packet delay. MPLS remains independent of the layer 2 and 3 protocols. IP packets are encapsulated, labeled, and switched between the source and destination PEs. Each CE and PE pair creates a local loop/access.
Note that an edge device can belong to multiple VPNs as illustrated by the PE3 and PE4 devices.
The NBIP-VPNS managed solution facilitates the shift of an Agency's capital and operational expenditure burdens to the Networx contractor. The contractor's core MPLS infrastructure can be used to create Agency specific topologies from partially-meshed to fully-meshed networks.
NBIP-VPNS supports a complete set of Agency site types:
NBIP-VPNS allows Agencies to interconnect sites served by ATMS, FRS, PLS, and Ethernet services. The MPLS backbone creates virtual circuits between MPLS-enabled endpoints on the network, and provides the ability to establish Classes of Service (CoS) categorized by the type of traffic. The classification of traffic is defined at the Agency SED, and may be categorized as:
End-to-end Quality of Service (QoS) can be provided through traffic classification and prioritization at the CE, PE, or core P devices (see the example figure). Agencies will receive customized NBIP-VPNS solutions that meet the Agency's specific requirements.
NBIP-VPNS features are available that include:
Basic service level agreements (SLAs) supported include:
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for NBIP-VPNS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for NBIP-VPNS.
For more information on the general NBIP-VPNS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.7.3 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.7.3 for pricing.
NBIP-VPNS provides network-based private data transport between user locations. The pricing associated with NBIP-VPNS is based on a number of factors such as number of sites, bandwidth requirements, security services, and the type of access. CLINs are distinguished by access type:
NBIP-VPNS is equivalent to FTS2001 services such as Private IP (PIP), Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), and Very high performance Backbone Network Service (VBNS).
Price components required for full end-to-end service for Domestic and Non-Domestic NBIP-VPNS:
Example 1: NBIP-VPNS CONUS Dedicated T1
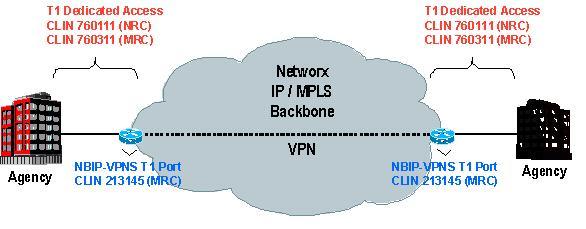
This document only addresses the NBIP-VPN service at contract award. Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for NBIP-VPNS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for NBIP-VPNS.
For more information on the general NBIP-VPNS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.7.3 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.7.3 for pricing.